Class-based tunnel selection (CBTS) is an MPLS Traffic Engineering (TE) feature where you can forward traffic with certain EXP values onto different TE tunnels. You can assign one or more EXP values to a tunnel and assign a TE tunnel as the default. This way, you don’t have to assign all EXP values separately.
CBTS is a local mechanism on the headend router and only works for TE tunnels between the same headend and tailend router. We call this “set” of TE tunnels a bundle. There is one master tunnel that bundles the member tunnels.

CBTS is not a routing solution. You still need something like a static route or autoroute to send traffic down the master tunnel interface. When the headend router receives traffic in the master tunnel interface, it will automatically select the correct member tunnel interface based on the EXP value of the packet. That’s the only thing CBTS does.
Packets can enter the headend router through multiple incoming interfaces, and not all packets may be marked correctly if you deal with different customers. When you configure MQC to (re)mark packets on the headend router, CBTS will use the new EXP values to decide what TE tunnel to use.
Configuration
Let’s see how we configure CBTS. This is the topology I’ll use:
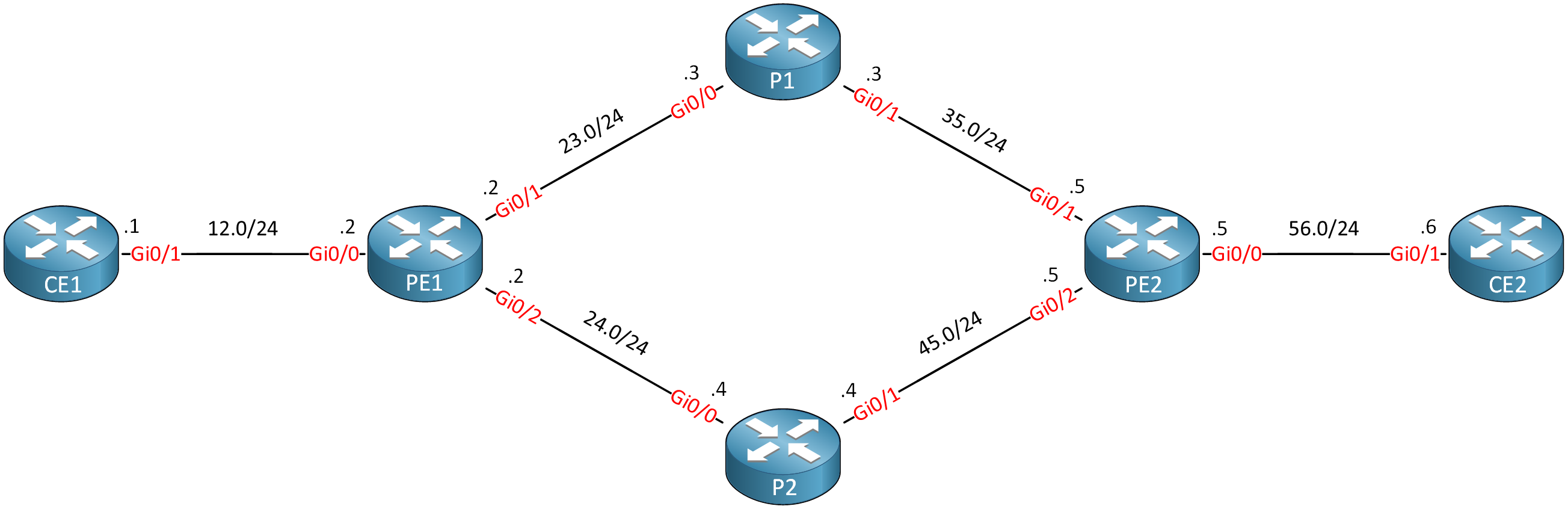
Routers PE1, P1, P2, and PE2 run MPLS TE. I have two TE tunnels from PE1 to PE2. I use IOSv Software (VIOS-ADVENTERPRISEK9-M), Version 15.9(3)M4 on all routers.
- Configurations
- CE1
- CE2
- P1
- P2
- PE1
- PE2
Want to take a look for yourself? Here you will find the startup configuration of each device.
Let’s say we use tunnel 1 for VoIP traffic and tunnel 2 for all other traffic. You would probably use an explicit path option in a production network so that the tunnels use two different paths through the network. For this lab, we won’t need this.
There are two things we need to configure:
- Assign EXP values to member tunnel interfaces.
- Create a new master tunnel interface and add the member tunnel interfaces.
Let’s configure our two member tunnels so that packets with EXP value 5 end up in tunnel 1 and everything else ends up in tunnel 2:
PE1(config)#interface Tunnel 1
PE1(config-if)#tunnel mpls traffic-eng exp 5PE1(config)#interface Tunnel 2
PE1(config-if)#tunnel mpls traffic-eng exp default Now we configure the master TE tunnel:
PE1(config)#interface Tunnel 10
PE1(config-if)#ip unnumbered Loopback0
PE1(config-if)#tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng
PE1(config-if)#tunnel destination 6.6.6.6
PE1(config-if)#tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce
PE1(config-if)#tunnel mpls traffic-eng exp-bundle master
PE1(config-if)#tunnel mpls traffic-eng exp-bundle member Tunnel1
PE1(config-if)#tunnel mpls traffic-eng exp-bundle member Tunnel2The configuration of the master tunnel interface is the same as the member tunnel interfaces. We turn this tunnel interface into a master tunnel with the tunnel mpls traffic-eng exp-bundle master command. We add the two member tunnel interfaces with the tunnel mpls traffic-eng exp-bundle member command.
I also enable autoroute on the master tunnel interface. That’s all you need to configure.
- Unit 1: Introduction
- Unit 2: LDP (Label Distribution Protocol)
- Unit 3: MPLS VPN
- VRFs (Virtual Routing and Forwarding)
- MPLS L3 VPN Explained
- MPLS L3 VPN Configuration
- MPLS L3 VPN BGP Allow AS in
- MPLS L3 VPN BGP AS Override
- MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE RIP
- MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE EIGRP
- MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE OSPF
- MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Default Route
- MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Global Default Route
- MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Sham Link
- VRF Lite Route Leaking
- MPLS VPN Extranet Route Leaking
- MPLS VPN VRF Export Map
- MPLS VPN VRF Import Map
- MPLS over FlexVPN
- Unit 4: MPLS L2 Encapsulation
- Unit 5: IPv6 MPLS
- Unit 6: MPLS Traffic Engineering (TE)
- Introduction to MPLS Traffic Engineering (TE)
- MPLS Traffic Engineering (TE) IS-IS Configuration
- MPLS Traffic Engineering (TE) OSPF Configuration
- MPLS TE RSVP-TE
- MPLS TE Static Routes
- MPLS TE Policy Based Routing (PBR)
- MPLS TE Autoroute Announce
- MPLS TE Autoroute Destination
- MPLS TE Autoroute Metric
- MPLS TE Unequal Cost Load Balancing
- MPLS TE Load Balancing between IGP and TE
- MPLS TE Forwarding Adjacency
- MPLS TE Path Options Explicit
- MPLS TE Class-Based Tunnel Selection (CBTS)
- MPLS TE Metric
- MPLS TE Setup and Hold Priority
- MPLS TE Attribute Flag and Affinity
- MPLS TE Reoptimization
- MPLS TE Fast Reroute (FRR)
- MPLS TE Fast Reroute Path Link Protection
- MPLS TE Fast Reroute Path Node Protection
- MPLS TE FRR RSVP Hello Support
- MPLS TE DiffServ Aware (DS-TE) Traditional
- MPLS TE Diffserv-Aware (DS-TE) IETF Mode
- MPLS VPN over MPLS TE Tunnels
- MPLS TE Per VRF TE tunnel