As we have seen in the MPLS TE configuration lesson, no traffic is forwarded down an MPLS Traffic Engineering (TE) tunnel by default. It’s similar to a GRE tunnel. The tunnel is there but doesn’t do anything. You have to configure routing to forward traffic down the tunnel.
We have multiple options to route traffic down a TE tunnel. One of the options is Policy Based Routing (PBR). There is nothing special about this configuration. It’s straightforward PBR. We match specific traffic with a route map and set the TE tunnel interface as the next hop.
Configuration
This is the topology we’ll use:
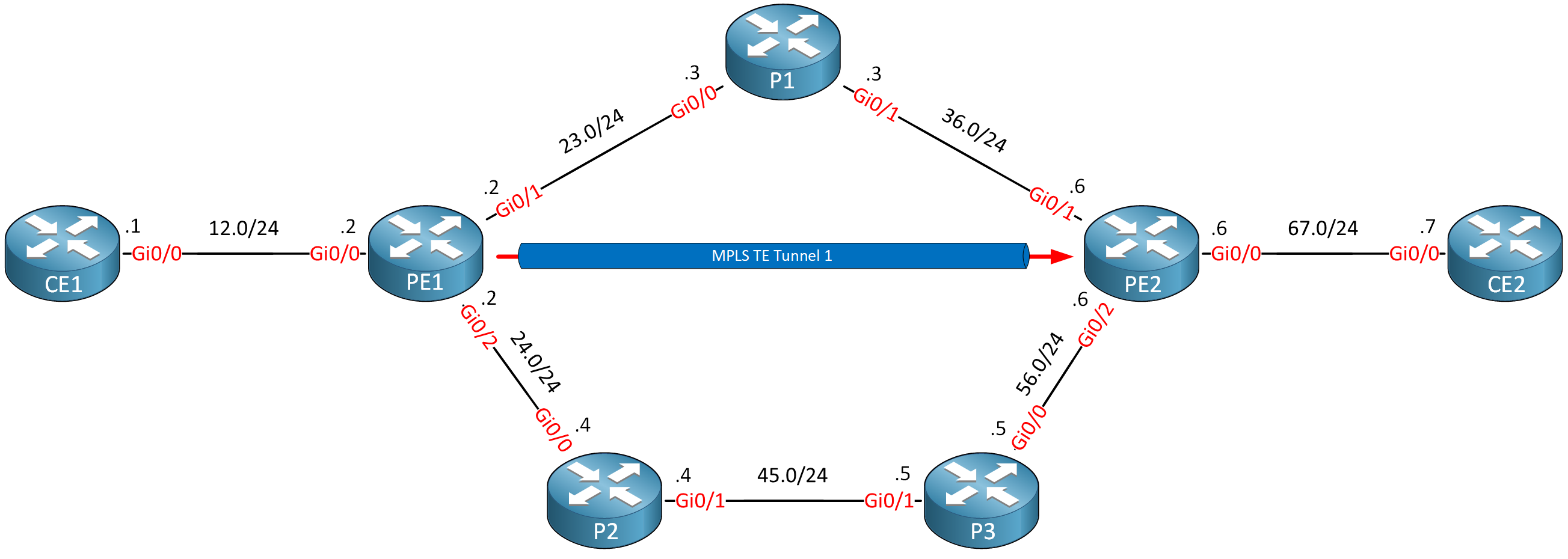
Routers PE1, P1, P2, P3, and PE2 run MPLS TE. We have a tunnel from PE1 to PE2. I use Cisco IOS Software, IOSv Software (VIOS-ADVENTERPRISEK9-M), Version 15.9(3)M4.
- Configurations
- CE1
- CE2
- P1
- P2
- P3
- PE1
- PE2
Want to take a look for yourself? Here you will find the startup configuration of each device.
Here is the routing table of PE1:
PE1#show ip route isis
1.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
i L2 1.1.1.1 [115/20] via 192.168.12.1, 00:04:02, GigabitEthernet0/0
3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
i L2 3.3.3.3 [115/20] via 192.168.23.3, 00:03:52, GigabitEthernet0/1
4.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
i L2 4.4.4.4 [115/20] via 192.168.24.4, 00:04:12, GigabitEthernet0/2
5.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
i L2 5.5.5.5 [115/30] via 192.168.24.4, 00:03:52, GigabitEthernet0/2
6.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
i L2 6.6.6.6 [115/30] via 192.168.23.3, 00:03:14, GigabitEthernet0/1
7.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
i L2 7.7.7.7 [115/40] via 192.168.23.3, 00:03:14, GigabitEthernet0/1
i L2 192.168.36.0/24 [115/20] via 192.168.23.3, 00:03:52, GigabitEthernet0/1
i L2 192.168.45.0/24 [115/20] via 192.168.24.4, 00:04:12, GigabitEthernet0/2
i L2 192.168.56.0/24 [115/30] via 192.168.24.4, 00:03:14, GigabitEthernet0/2
[115/30] via 192.168.23.3, 00:03:14, GigabitEthernet0/1
i L2 192.168.67.0/24 [115/30] via 192.168.23.3, 00:03:14, GigabitEthernet0/1As you can see above, we don’t use the tunnel interface. We’ll configure PBR to forward some traffic down our TE tunnel.
Let’s start with an access-list that matches traffic between the loopback interfaces of CE1 and CE2:
PE1(config)#ip access-list extended CE1_L0_CE2_L0
PE1(config-ext-nacl)#permit ip host 1.1.1.1 host 7.7.7.7And we’ll create a route-map that matches the access-list and sets the tunnel as the next hop:
PE1(config)#route-map CE1_CE2_TUNNEL1 permit 10
PE1(config-route-map)#match ip address CE1_L0_CE2_L0
PE1(config-route-map)#set interface Tunnel 1We’ll attach the route-map on the interface that connects to CE1:
PE1(config)#interface GigabitEthernet 0/0
PE1(config-if)#ip policy route-map CE1_CE2_TUNNEL1This completes our configuration.
Verification
Let’s verify our work. I’ll enable a debug so we can see it in action:
PE1#debug ip policy
Policy routing debugging is onLet’s send a ping from CE1 to CE2:
CE1#ping 7.7.7.7 source 1.1.1.1 repeat 1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 1, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 7.7.7.7, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 1.1.1.1
!
Success rate is 100 percent (1/1), round-trip min/avg/max = 8/8/8 msThis is what we see on our console:
PE1#
IP: s=1.1.1.1 (GigabitEthernet0/0), d=7.7.7.7, len 100, FIB policy match
IP: s=1.1.1.1 (GigabitEthernet0/0), d=7.7.7.7, len 100, PBR Counted
IP: s=1.1.1.1 (GigabitEthernet0/0), d=7.7.7.7 (Tunnel1), len 100, FIB policy routedThis is looking good. Traffic is forwarded down the tunnel. We can also verify this by looking at our route-map:
PE1#show route-map
route-map CE1_CE2_TUNNEL1, permit, sequence 10
Match clauses:
ip address (access-lists): CE1_L0_CE2_L0
Set clauses:
interface Tunnel1
Interface tracking current: NULL
Tunnel1, adj_lh:0,oce:0,status:0
Policy routing matches: 1 packets, 114 bytesThat’s all there is to it.
- Configurations
- CE1
- CE2
- P1
- P2
- P3
- PE1
- PE2
Want to take a look for yourself? Here you will find the final configuration of each device.
Conclusion
You have learned to use PBR to forward traffic down an MPLS TE tunnel. I hope you enjoyed this lesson. If you have any questions, please leave a comment.
- Unit 1: Introduction
- Unit 2: LDP (Label Distribution Protocol)
- Unit 3: MPLS VPN
- VRFs (Virtual Routing and Forwarding)
- MPLS L3 VPN Explained
- MPLS L3 VPN Configuration
- MPLS L3 VPN BGP Allow AS in
- MPLS L3 VPN BGP AS Override
- MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE RIP
- MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE EIGRP
- MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE OSPF
- MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Default Route
- MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Global Default Route
- MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Sham Link
- VRF Lite Route Leaking
- MPLS VPN Extranet Route Leaking
- MPLS VPN VRF Export Map
- MPLS VPN VRF Import Map
- MPLS over FlexVPN
- Unit 4: MPLS L2 Encapsulation
- Unit 5: IPv6 MPLS
- Unit 6: MPLS Traffic Engineering (TE)
- Introduction to MPLS Traffic Engineering (TE)
- MPLS Traffic Engineering (TE) IS-IS Configuration
- MPLS Traffic Engineering (TE) OSPF Configuration
- MPLS TE RSVP-TE
- MPLS TE Static Routes
- MPLS TE Policy Based Routing (PBR)
- MPLS TE Autoroute Announce
- MPLS TE Autoroute Destination
- MPLS TE Autoroute Metric
- MPLS TE Unequal Cost Load Balancing
- MPLS TE Load Balancing between IGP and TE
- MPLS TE Forwarding Adjacency
- MPLS TE Path Options Explicit
- MPLS TE Class-Based Tunnel Selection (CBTS)
- MPLS TE Metric
- MPLS TE Setup and Hold Priority
- MPLS TE Attribute Flag and Affinity
- MPLS TE Reoptimization
- MPLS TE Fast Reroute (FRR)
- MPLS TE Fast Reroute Path Link Protection
- MPLS TE Fast Reroute Path Node Protection
- MPLS TE FRR RSVP Hello Support
- MPLS TE DiffServ Aware (DS-TE) Traditional
- MPLS TE Diffserv-Aware (DS-TE) IETF Mode
- MPLS VPN over MPLS TE Tunnels
- MPLS TE Per VRF TE tunnel