Any Transport over MPLS (AToM) will transport layer 2 frames over an MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) network. This will allow service providers to connect layer 2 networks of customers transparently by using their MPLS backbone. AToM can transport the following:
- ATM AAL5
- ATM Cell Relay
- Ethernet
- Frame Relay
- PPP
- HDLC
I will give you an example of how to configure AToM to transport Ethernet over the MPLS backbone. We will use the following topology to do this:
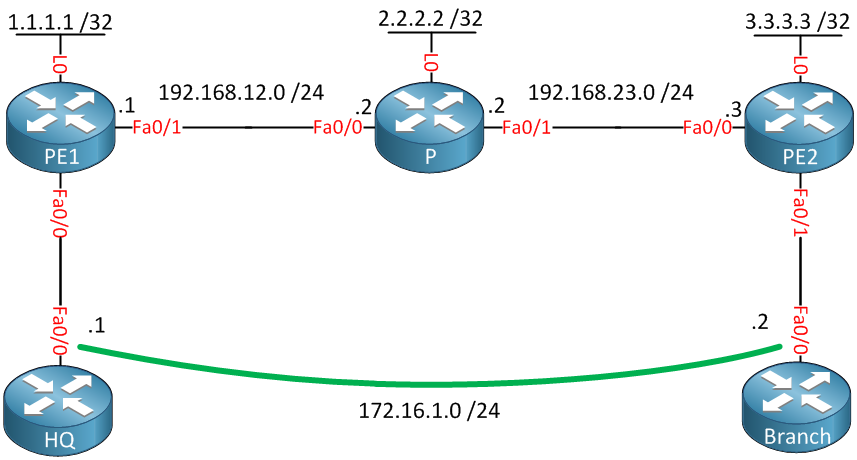
Above, you see a small MPLS backbone that consists of the PE1, P, and PE2 routers. This ISP only has one customer that has an HQ and Branch. The customer wants to have the HQ and Branch router to be in the same layer 2 segment.
Configuration
First, we will enable OSPF to advertise the loopback interfaces. These will be used as the router ID for MPLS LDP:
PE1(config)#router ospf 1
PE1(config-router)#network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
PE1(config-router)#network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0P(config)#router ospf 1
P(config-router)#network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
P(config-router)#network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
P(config-router)#network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0PE2(config)#router ospf 1
PE2(config-router)#network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
PE2(config-router)#network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 area 0Now we will enable MPLS LDP on the interfaces connecting the PE1, P, and PE2 routers:
PE1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/1
PE1(config-if)#mpls ipP(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
P(config-if)#mpls ip
P(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/1
P(config-if)#mpls ip PE2(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
PE2(config-if)#mpls ipJust to be sure let’s verify that we have LDP neighbors:
P#show mpls ldp neighbor | include Peer
Peer LDP Ident: 1.1.1.1:0; Local LDP Ident 2.2.2.2:0
Peer LDP Ident: 3.3.3.3:0; Local LDP Ident 2.2.2.2:0That seems to be the case! Now we can configure AToM so that the HQ and Branch routers are able to reach each other:
- Unit 1: Introduction
- Unit 2: LDP (Label Distribution Protocol)
- Unit 3: MPLS VPN
- VRFs (Virtual Routing and Forwarding)
- MPLS L3 VPN Explained
- MPLS L3 VPN Configuration
- MPLS L3 VPN BGP Allow AS in
- MPLS L3 VPN BGP AS Override
- MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE RIP
- MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE EIGRP
- MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE OSPF
- MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Default Route
- MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Global Default Route
- MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Sham Link
- VRF Lite Route Leaking
- MPLS VPN Extranet Route Leaking
- MPLS VPN VRF Export Map
- MPLS VPN VRF Import Map
- MPLS over FlexVPN
- Unit 4: MPLS L2 Encapsulation
- Unit 5: IPv6 MPLS
- Unit 6: MPLS Traffic Engineering (TE)
- Introduction to MPLS Traffic Engineering (TE)
- MPLS Traffic Engineering (TE) IS-IS Configuration
- MPLS Traffic Engineering (TE) OSPF Configuration
- MPLS TE RSVP-TE
- MPLS TE Static Routes
- MPLS TE Policy Based Routing (PBR)
- MPLS TE Autoroute Announce
- MPLS TE Autoroute Destination
- MPLS TE Autoroute Metric
- MPLS TE Unequal Cost Load Balancing
- MPLS TE Load Balancing between IGP and TE
- MPLS TE Forwarding Adjacency
- MPLS TE Path Options Explicit
- MPLS TE Class-Based Tunnel Selection (CBTS)
- MPLS TE Metric
- MPLS TE Setup and Hold Priority
- MPLS TE Attribute Flag and Affinity
- MPLS TE Reoptimization
- MPLS TE Fast Reroute (FRR)
- MPLS TE Fast Reroute Path Link Protection
- MPLS TE Fast Reroute Path Node Protection
- MPLS TE FRR RSVP Hello Support
- MPLS TE DiffServ Aware (DS-TE) Traditional
- MPLS TE Diffserv-Aware (DS-TE) IETF Mode
- MPLS VPN over MPLS TE Tunnels
- MPLS TE Per VRF TE tunnel