In the OSPF virtual link lesson, I explained how to configure a virtual link, but I didn’t show how to enable virtual link authentication. That’s what we are going to cover in this lesson.
There are two authentication methods:
- Plain text
- MD5
I’ll show you both options.
Configuration
Here is the topology we will use:
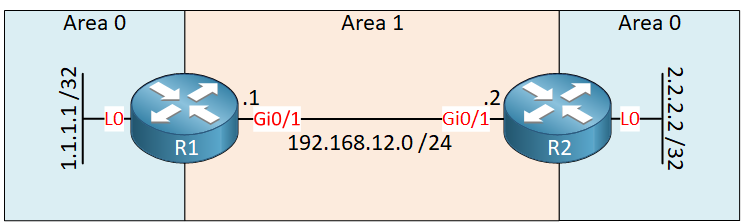
We have two routers running OSPF. Area 0 is discontinuous, so we need a virtual link through area 1 to fix this.
- Configurations
- R1
- R2
Want to take a look for yourself? Here you will find the startup configuration of each device.
Let’s see if we can authenticate this virtual link.
Plain Text Authentication
There are two things we need to do to enable authentication:
- Enable authentication for area 0: the virtual link belongs to area 0, so you need authentication for the backbone area, not the area that the virtual link goes through.
- Set the authentication password for the virtual link.
Only two commands are required to achieve this:
R1(config)#router ospf 1
R1(config-router)#area 0 authentication
R1(config-router)#area 1 virtual-link 2.2.2.2 authentication-key NWLR2(config)#router ospf 1
R2(config-router)#area 0 authentication
R2(config-router)#area 1 virtual-link 1.1.1.1 authentication-key NWLLet’s see if it works. Let’s reset the OSPF process:
R1#clear ip ospf process
Reset ALL OSPF processes? [no]: yesAfter a few seconds, our virtual link is back:
R1#
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 2.2.2.2 on OSPF_VL0 from LOADING to FULL, Loading DoneLet’s verify that authentication is enabled:
R1#show ip ospf virtual-links
Virtual Link OSPF_VL0 to router 2.2.2.2 is up
Run as demand circuit
DoNotAge LSA allowed.
Transit area 1, via interface GigabitEthernet0/1
Topology-MTID Cost Disabled Shutdown Topology Name
0 1 no no Base
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT_TO_POINT,
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
Hello due in 00:00:01
Adjacency State FULL (Hello suppressed)
Index 1/1/2, retransmission queue length 0, number of retransmission 0
First 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0) Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last retransmission scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last retransmission scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Simple password authentication enabledThere we go, above you can see that simple password authentication is enabled.
- Configurations
- R1
- R2
Want to take a look for yourself? Here you will find the final configuration of each device.
MD5 Authentication
Let’s try MD5 authentication. The configuration is similar:
R1(config)#router ospf 1
R1(config-router)#area 0 authentication message-digest
R1(config-router)#area 1 virtual-link 2.2.2.2 message-digest-key 1 md5 NWLR2(config)#router ospf 1
R2(config-router)#area 0 authentication message-digest
R2(config-router)#area 1 virtual-link 1.1.1.1 message-digest-key 1 md5 NWLFirst, we need to configure area 0 to use MD5 authentication and then set the MD5 key for the virtual link.
Let’s see if it works:
R1#clear ip ospf process
Reset ALL OSPF processes? [no]: yesThe virtual link appears again:
R1#
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 2.2.2.2 on OSPF_VL0 from LOADING to FULL, Loading DoneAnd we can verify that it works with the show command:
R1#show ip ospf virtual-links
Virtual Link OSPF_VL0 to router 2.2.2.2 is up
Run as demand circuit
DoNotAge LSA allowed.
Transit area 1, via interface GigabitEthernet0/1
Topology-MTID Cost Disabled Shutdown Topology Name
0 1 no no Base
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT_TO_POINT,
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
Hello due in 00:00:02
Adjacency State FULL (Hello suppressed)
Index 1/1/2, retransmission queue length 0, number of retransmission 0
First 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0) Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last retransmission scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last retransmission scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Cryptographic authentication enabled
Youngest key id is 1Cryptographic authentication means MD5 authentication is enabled. That’s all there is to it!
Conclusion
You have now learned how to configure plain text or MD5 authentication for your OSPF virtual links. Although the configuration is pretty straightforward, one thing to be aware of is that the virtual link belongs to area 0…not the area it goes through. Make sure you enable authentication for area 0, not for the area that the virtual link uses.
Unit 1: Introduction to OSPF
- Introduction to OSPF
- Basic OSPF Configuration
- OSPF Multi Area Configuration
- OSPF Reference Bandwidth
- OSPF Plain Text Authentication
- OSPF MD5 Authentication
- OSPF SHA-HMAC Authentication
- OSPF TTL Security Check
- OSPF Default Route
Unit 2: OSPF Neighbor Adjacency
- OSPF LSA Types
- OSPF LSAs and LSDB Flooding
- OSPF Hello and Dead Interval
- OSPF Router ID
- OSPF Packets and Neighbor Discovery
- OSPF DR/BDR Election
- OSPF Passive Interface
- Troubleshooting OSPF Neighbor Adjacency
Unit 3: OSPF Network Types
- OSPF Non-Broadcast Network Type
- OSPF Broadcast Network Type
- OSPF Point-to-Multipoint Network Type
- OSPF Point-to-Multipoint Non-Broadcast Network Type
- OSPF Point-to-Point Network Type
- OSPF Next Hop with Network Types
Unit 4: OSPF Stub Areas
- Introduction to OSPF Stub Areas
- How to configure OSPF Stub Area
- How to configure OSPF Totally Stub
- How to configure OSPF NSSA (Not So Stubby) Area
- How to configure OSPF Totally NSSA (Not So Stubby) Area
- OSPF NSSA P-bit explained
Unit 5: Advanced OSPF Topics
- OSPF Summarization
- OSPF Distribute-List Filtering
- OSPF LSA Type 3 Filtering
- OSPF LSA Type 5 Filtering
- OSPF Virtual Link
- OSPF Virtual Link Authentication
- OSPF Path Selection Explained
- How to read the OSPF Database
- OSPFv3 for IPv4
- Troubleshooting OSPF Route Advertisement
- OSPF SPF Scheduling and Throttling
- OSPF LSA Throttling
- OSPF Incremental SPF
- OSPF Prefix Suppression
- OSPF Stub Router
- OSPF Graceful Shutdown
- OSPF Graceful Restart
- OSPF Loop-Free Alternate (LFA) Fast Reroute (FRR)
- OSPF Remote Loop-Free Alternate (LFA) Fast Reroute (FRR)