OSPF has a stub router feature (don’t confuse this with stub areas) that lets you prevent a router from being a transit router. Here’s an example of why you might want to use this:
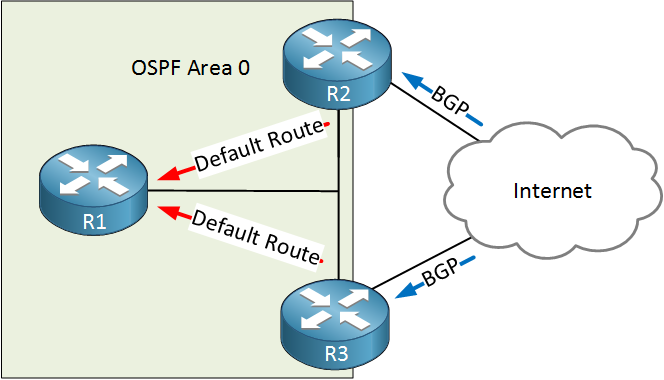
Above we have three routers, running OSPF. R2 and R3 advertise a default route in OSPF and also run BGP. OSPF converges faster than BGP so if you reload R2 or R3, it is possible that packets get dropped because BGP hasn’t converged yet but OSPF is already advertising its default route. To prevent this, we can configure OSPF to (temporarily) set the metric to its maximum value. You can do this until BGP converges, for a certain period, or even permanent.
Let’s look at a configuration example. I use the following topology:
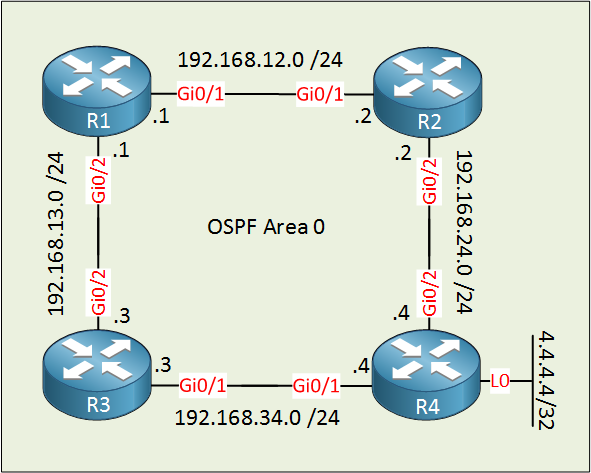
Above we have four routers in area 0. R4 has a loopback interface that we try to reach from R1. I increased the cost of R3’s Gigabit 0/1 interface so that the path through R2 is preferred:
R1#show ip route ospf
4.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 4.4.4.4 [110/3] via 192.168.12.2, 00:01:44, GigabitEthernet0/1
O 192.168.24.0/24 [110/2] via 192.168.12.2, 00:01:44, GigabitEthernet0/1
O 192.168.34.0/24 [110/3] via 192.168.12.2, 00:01:44, GigabitEthernet0/1As you can see above, R1 uses R2 to reach 4.4.4.4/32. Here’s the router LSA that R2 advertises:
R1#show ip ospf database router 2.2.2.2
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 0)
LS age: 139
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Router Links
Link State ID: 2.2.2.2
Advertising Router: 2.2.2.2
LS Seq Number: 80000006
Checksum: 0xF322
Length: 48
Number of Links: 2
Link connected to: a Transit Network
(Link ID) Designated Router address: 192.168.24.4
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 192.168.24.2
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Link connected to: a Transit Network
(Link ID) Designated Router address: 192.168.12.2
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 192.168.12.2
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1All links that R2 advertises have a cost of one. Let’s see if we can configure R2 so that it doesn’t want to be a transit router. We can use the max-metric router-lsa command to implement this:
R2(config)#router ospf 1
(config-router)#max-metric router-lsa ?
external-lsa Override external-lsa metric with max-metric value
include-stub Set maximum metric for stub links in router-LSAs
on-startup Set maximum metric temporarily after reboot
summary-lsa Override summary-lsa metric with max-metric value
<cr>There are a number of options you can choose from. The on-startup options let you set the maximum metric temporarily when OSPF has started or until BGP has converged. We will keep it simple for now and enable max-metric permanently:
R2(config-router)#max-metric router-lsaWe can verify that it is enabled:
R2#show ip ospf | begin Originating
Originating router-LSAs with maximum metric
Condition: always, State: activeR1 will now prefer R3 instead of R2:
R1#show ip route ospf
4.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 4.4.4.4 [110/12] via 192.168.13.3, 00:00:09, GigabitEthernet0/2
O 192.168.24.0/24 [110/12] via 192.168.13.3, 00:00:09, GigabitEthernet0/2
O 192.168.34.0/24 [110/11] via 192.168.13.3, 00:00:09, GigabitEthernet0/2Let’s take a closer look to see what R2 has changed in its router LSA:
R1#show ip ospf database router 2.2.2.2
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 0)
LS age: 32
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Router Links
Link State ID: 2.2.2.2
Advertising Router: 2.2.2.2
LS Seq Number: 80000007
Checksum: 0xC155
Length: 48
Number of Links: 2
Link connected to: a Transit Network
(Link ID) Designated Router address: 192.168.24.4
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 192.168.24.2
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 65535
Link connected to: a Transit Network
(Link ID) Designated Router address: 192.168.12.2
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 192.168.12.2
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 65535As you can see above, the metric is set to 65535 which makes it very unlikely that R2 will be used as a transit router. I enabled this permanently but if you want to enable it temporarily, you can do it like this:
R1(config-router)#max-metric router-lsa on-startup ?
<5-86400> Time, in seconds, router-LSAs are originated with max-metric
wait-for-bgp Let BGP decide when to originate router-LSA with normal metricIf you use the wait-for-bgp option. The router will set the max metric until BGP has converged or until 10 minutes have elapsed since OSPF started. That’s all there is to it!
- Configurations
- R1
- R2
- R3
- R4
Unit 1: Introduction to OSPF
- Introduction to OSPF
- Basic OSPF Configuration
- OSPF Multi Area Configuration
- OSPF Reference Bandwidth
- OSPF Plain Text Authentication
- OSPF MD5 Authentication
- OSPF SHA-HMAC Authentication
- OSPF TTL Security Check
- OSPF Default Route
Unit 2: OSPF Neighbor Adjacency
- OSPF LSA Types
- OSPF LSAs and LSDB Flooding
- OSPF Hello and Dead Interval
- OSPF Router ID
- OSPF Packets and Neighbor Discovery
- OSPF DR/BDR Election
- OSPF Passive Interface
- Troubleshooting OSPF Neighbor Adjacency
Unit 3: OSPF Network Types
- OSPF Non-Broadcast Network Type
- OSPF Broadcast Network Type
- OSPF Point-to-Multipoint Network Type
- OSPF Point-to-Multipoint Non-Broadcast Network Type
- OSPF Point-to-Point Network Type
- OSPF Next Hop with Network Types
Unit 4: OSPF Stub Areas
- Introduction to OSPF Stub Areas
- How to configure OSPF Stub Area
- How to configure OSPF Totally Stub
- How to configure OSPF NSSA (Not So Stubby) Area
- How to configure OSPF Totally NSSA (Not So Stubby) Area
- OSPF NSSA P-bit explained
Unit 5: Advanced OSPF Topics
- OSPF Summarization
- OSPF Distribute-List Filtering
- OSPF LSA Type 3 Filtering
- OSPF LSA Type 5 Filtering
- OSPF Virtual Link
- OSPF Virtual Link Authentication
- OSPF Path Selection Explained
- How to read the OSPF Database
- OSPFv3 for IPv4
- Troubleshooting OSPF Route Advertisement
- OSPF SPF Scheduling and Throttling
- OSPF LSA Throttling
- OSPF Incremental SPF
- OSPF Prefix Suppression
- OSPF Stub Router
- OSPF Graceful Shutdown
- OSPF Graceful Restart
- OSPF Loop-Free Alternate (LFA) Fast Reroute (FRR)
- OSPF Remote Loop-Free Alternate (LFA) Fast Reroute (FRR)