In a previous lesson, I explained the OSPF Non-Broadcast Network Type. Now it’s time for the broadcast network type. If you understand non-broadcast, then this one is easy. It’s the EXACT same thing, except we don’t have to configure neighbors. OSPF will use multicast and discover OSPF neighbors automatically. The broadcast network type is the default for Ethernet interfaces.
This is the topology that we’ll use:
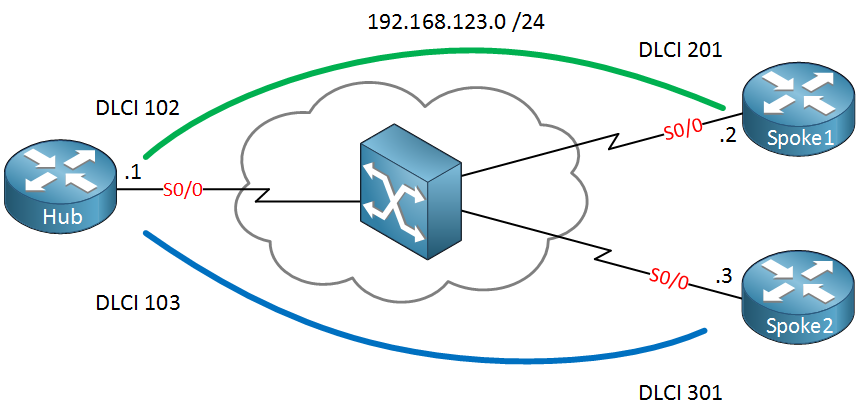
Hub(config)#interface serial 0/0
Hub(config-if)#ip address 192.168.123.1 255.255.255.0
Hub(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay
Hub(config-if)#ip ospf network broadcast
Hub(config-if)#exit
Hub(config)#router ospf 1
Hub(config-router)#network 192.168.123.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Here is the configuration of the Hub router. I used the ip ospf network broadcast command to change the OSPF network type. Here are the spoke routers:
Spoke1(config)#interface serial 0/0
Spoke1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.123.2 255.255.255.0
Spoke1(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay
Spoke1(config-if)#ip ospf network broadcast
Spoke1(config-if)#ip ospf priority 0
Spoke1(config-if)#exit
Spoke1(config)#router ospf 1
Spoke1(config-router)#network 192.168.123.0 0.0.0.255 area 0Spoke2(config)#interface serial 0/0
Spoke2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.123.3 255.255.255.0
Spoke2(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay
Spoke2(config-if)#ip ospf network broadcast
Spoke2(config-if)#ip ospf priority 0
Spoke2(config-if)#exit
Spoke2(config)#router ospf 1
Spoke2(config-router)#network 192.168.123.0 0.0.0.255 area 0Make sure you set the priority to 0 for the spoke routers. We don’t want them to become the DR or BDR!
Make sure you have a frame-relay map statement with the broadcast keyword, or you won’t be able to send multicast on your frame-relay network. By default Inverse ARP is enabled and will do this for you…if you don’t have inverse ARP, make sure you add it!
Hub#show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
192.168.123.2 0 FULL/DROTHER 00:00:30 192.168.123.2 Serial0/0
192.168.123.3 0 FULL/DROTHER 00:00:35 192.168.123.3 Serial0/0Here you can see that the hub router is the DR because the spoke routers are DROTHERS.
Unit 1: Introduction to OSPF
- Introduction to OSPF
- Basic OSPF Configuration
- OSPF Multi Area Configuration
- OSPF Reference Bandwidth
- OSPF Plain Text Authentication
- OSPF MD5 Authentication
- OSPF SHA-HMAC Authentication
- OSPF TTL Security Check
- OSPF Default Route
Unit 2: OSPF Neighbor Adjacency
- OSPF LSA Types
- OSPF LSAs and LSDB Flooding
- OSPF Hello and Dead Interval
- OSPF Router ID
- OSPF Packets and Neighbor Discovery
- OSPF DR/BDR Election
- OSPF Passive Interface
- Troubleshooting OSPF Neighbor Adjacency
Unit 3: OSPF Network Types
- OSPF Non-Broadcast Network Type
- OSPF Broadcast Network Type
- OSPF Point-to-Multipoint Network Type
- OSPF Point-to-Multipoint Non-Broadcast Network Type
- OSPF Point-to-Point Network Type
- OSPF Next Hop with Network Types
Unit 4: OSPF Stub Areas
- Introduction to OSPF Stub Areas
- How to configure OSPF Stub Area
- How to configure OSPF Totally Stub
- How to configure OSPF NSSA (Not So Stubby) Area
- How to configure OSPF Totally NSSA (Not So Stubby) Area
- OSPF NSSA P-bit explained
Unit 5: Advanced OSPF Topics
- OSPF Summarization
- OSPF Distribute-List Filtering
- OSPF LSA Type 3 Filtering
- OSPF LSA Type 5 Filtering
- OSPF Virtual Link
- OSPF Virtual Link Authentication
- OSPF Path Selection Explained
- How to read the OSPF Database
- OSPFv3 for IPv4
- Troubleshooting OSPF Route Advertisement
- OSPF SPF Scheduling and Throttling
- OSPF LSA Throttling
- OSPF Incremental SPF
- OSPF Prefix Suppression
- OSPF Stub Router
- OSPF Graceful Shutdown
- OSPF Graceful Restart
- OSPF Loop-Free Alternate (LFA) Fast Reroute (FRR)
- OSPF Remote Loop-Free Alternate (LFA) Fast Reroute (FRR)