IPv6 Multicast BSR and RP Example
Multicast for IPv6 can be configured using static RPs, BSR or embedded RP. In this example I want to show you how to configure IPv6 multicast using BSR. This is the topology that I will use:
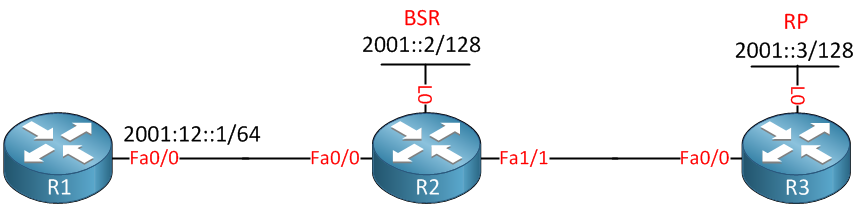
Above we have 3 routers. R1 will be the receiver of the multicast stream, R2 will be the BSR and R3 will be the RP. First we’ll have to do our homework and configure all IPv6 addresses on the interfaces:
R1(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
R1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R1(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001:12::1/64R2(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
R2(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R2(config-if)#ipv6 enable
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#interface fastEthernet 1/1
R2(config-if)#ipv6 enable
R2(config-if)#exit R2(config)#interface loopback 0 R2(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001::2/128R3(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
R3(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R3(config-if)#ipv6 enable
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#interface loopback 0
R3(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001::3/128With the IPv6 addresses up and running we can configure EIGRP to advertise the loopback interfaces of R2/R3 and the 2001:12::/64 network between R1/R2:
R1(config)#ipv6 router eigrp 1
R1(config-rtr)#router-id 1.1.1.1
R1(config-rtr)#no shutdown
R1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R1(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 1 R2(config)#ipv6 router eigrp 1
R2(config-rtr)#router-id 2.2.2.2
R2(config-rtr)#no shutdownR2(config)#interface loopback 0
R2(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 1
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R2(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 1
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#interface fastEthernet 1/1
R2(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 1 R3(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
R3(config)#ipv6 router eigrp 1
R3(config-rtr)#router-id 3.3.3.3
R3(config-rtr)#no shutdownR3(config)#interface loopback 0
R3(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 1
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R3(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 1 Because I don’t have any IPv4 addresses, I have to configure an EIGRP router ID myself. With the configuration above the 2001:12::/64, 2001::2/128, and 2001::3/128 networks should be reachable from any router. Now we can continue with our multicast setup:
R1,R2 & R3:
(config)#ipv6 multicast-routingFirst, enable multicast routing for IPv6, or we are going nowhere. The next step is to configure the RP and BSR:
R3(config)#ipv6 pim bsr candidate rp 2001::3
Use the ipv6 pim bsr candidate rp command to advertise R3 as the Rendezvous Point…
R2(config)#ipv6 pim bsr candidate bsr 2001::2And R2 as the BSR…now we’ll configure R1 to join a multicast group, I’ll use FF07::7 for this example:
R1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R1(config-if)#ipv6 mld join-group FF07::7Let’s see if R2 has found the RP:
R2#show ipv6 pim bsr rp-cache
PIMv2 BSR C-RP Cache
BSR Candidate RP Cache
Group(s) FF00::/8, RP count 1
RP 2001::3 SM
Priority 192, Holdtime 150
Uptime: 00:00:06, expires: 00:02:23R2 sees R3 as the RP for the entire multicast group range. We can also take a look at the multicast routing table:
R2#show ipv6 mroute
Multicast Routing Table
Flags: D - Dense, S - Sparse, B - Bidir Group, s - SSM Group,
C - Connected, L - Local, I - Received Source Specific Host Report,
P - Pruned, R - RP-bit set, F - Register flag, T - SPT-bit set,
J - Join SPT
Timers: Uptime/Expires
Interface state: Interface, State
(*, FF07::7), 00:03:53/never, RP 2001::3, flags: SCJ
Incoming interface: FastEthernet0/1
RPF nbr: FE80::C006:23FF:FE22:0
Immediate Outgoing interface list:
FastEthernet0/0, Forward, 00:03:53/neverAbove, we see that R2 built a (*,G) entry for FF07::7 towards the RP. Let’s generate some multicast traffic to see if it reaches R1:
R3#ping ff07::7
Output Interface: FastEthernet0/0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to FF07::7, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 2001::3
Reply to request 0 received from 2001:12::1, 8 ms
Reply to request 1 received from 2001:12::1, 8 ms
Reply to request 2 received from 2001:12::1, 8 ms
Reply to request 3 received from 2001:12::1, 4 ms
Reply to request 4 received from 2001:12::1, 8 ms
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 4/7/8 ms
5 multicast replies and 0 errors.Table of Content
Unit 1. Introduction to Multicast
Unit 2: IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol)
- Multicast IGMP Version 1
- Multicast IGMP Version 2
- Multicast IGMP Version 3
- Multicast IGMP Filter
- Multicast IGMP Proxy
Unit 3: Multicast L2
- Multicast IGMP Snooping
- IGMP Snooping without Router
- Multicast CGMP (Cisco Group Management Protocol)
Unit 4: Multicast L3
- Multicast Routing
- Multicast PIM Dense Mode
- Multicast PIM Sparse Mode
- Multicast PIM Sparse-Dense Mode
- Multicast PIM Auto RP
- Multicast PIM BSR (Bootstrap)
- RPF (Reverse Path Forwarding)
- Multicast Tunnel RPF Failure
- PIM Designated Router
- PIM Assert
- Multicast PIM Prune Override
- Multicast PIM Register Message
- Anycast RP
- Multicast MSDP SA Filtering
- Multicast Bidirectional PIM
- Multicast Stub Routing and IGMP Helper
- Source Specific Multicast
- Multicast PIM Accept RP
- Multicast PIM Accept Register
- Multicast Auto-RP Mapping agent behind Spoke
- PIM NBMA Mode
- Multicast Boundary Filtering
- Multicast PIM Snooping