IGMP Version 3
IGMP version 3 adds support for “source filtering”. IGMP version 1 and version 2 allow hosts to join multicast groups but they don’t check the source of the traffic. Any source is able to receive traffic to the multicast group(s) that they joined.
With source filtering, we can join multicast groups but only from specified source addresses. IGMP version 3 is a requirement for SSM (Source Specific Multicast).
Why is this useful? Let me give you an example:
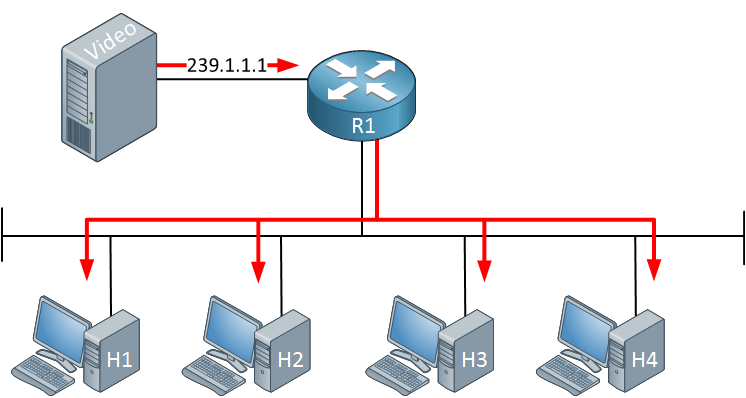
Above, we have a video server streaming multicast traffic on the network using destination address 239.1.1.1. Four hosts are listening to this traffic. Life is good. Suddenly, something happens:
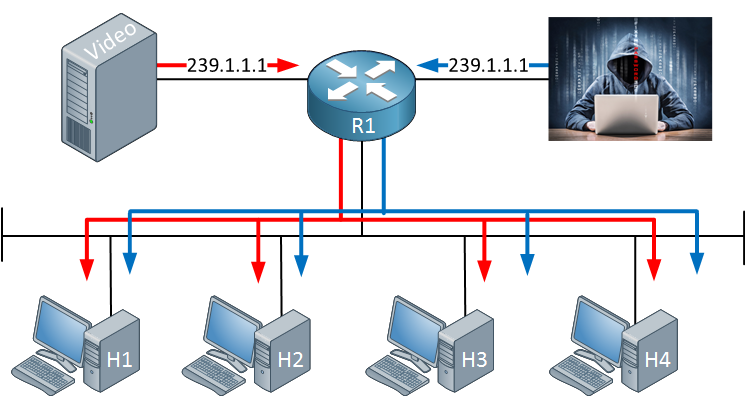
An attacker didn’t like the video stream and decided to stream his favorite video to destination address 239.1.1.1.1. Since we don’t check the source address, everyone will receive the traffic from our attacker. It’s also possible to send bogus traffic and create a DoS attack like this.
IGMP versions 1 and 2 don’t have any protection against this.
With IGMP version 3, our hosts can be configured to receive multicast traffic only from specified source addresses. Let’s see how this works. I’ll use the following topology for this:
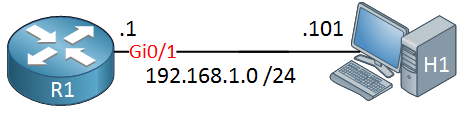
We will only use two devices: one multicast-enabled router and a host device. I’m using a Cisco router as the host device as well.
Let’s start with R1:
R1(config)#ip multicast-routing
R1(config)#interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
R1(config-if)#ip pim sparse-mode
R1(config-if)#ip igmp version 3Our router requires multicast routing, and PIM should be enabled on the interface. The default version of IGMP is 2, so we’ll change it to version 3. Before we let H1 join a multicast group, let’s enable debugging on both devices:
R1 & H1#debug ip igmp
IGMP debugging is onR1 will start sending membership general queries like the one below:
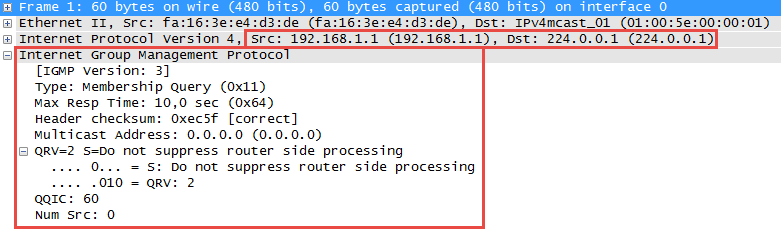
Let’s configure H1 to join a multicast group:
H1(config)#interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
H1(config-if)#ip igmp join-group 239.1.1.1 ?
source Include SSM source
<cr>Besides configuring a group, I can configure the host to include a source address. Let’s pick something:
H1(config-if)#ip igmp join-group source 239.1.1.1 source 1.1.1.1H1 will now include the source address in its membership report messages. Here’s what you will see on the console:
H1#
IGMP(0): WAVL Insert group: 239.1.1.1 interface: GigabitEthernet0/1Successful
IGMP(0): Create source 1.1.1.1
IGMP(0): Building v3 Report on GigabitEthernet0/1
IGMP(0): Add Group Record for 239.1.1.1, type 5
IGMP(0): Add Source Record 1.1.1.1
IGMP(0): Add Group Record for 239.1.1.1, type 6
IGMP(0): No sources to add, group record removed from report
IGMP(0): Send unsolicited v3 Report with 1 group records on GigabitEthernet0/1
IGMP(0): Building v3 Report on GigabitEthernet0/1
IGMP(0): Add Group Record for 239.1.1.1, type 5
IGMP(0): Add Source Record 1.1.1.1
IGMP(0): Add Group Record for 239.1.1.1, type 6
IGMP(0): No sources to add, group record removed from report
IGMP(0): Send unsolicited v3 Report with 1 group records on GigabitEthernet0/1H1 sends two membership report messages. The first message includes the multicast group and source addresses we want to receive. The second message includes the “mode”. There are two modes:
- Include: this is a list of source addresses that we accept multicast traffic from. Everything else should not be forwarded.
- Exclude: this is a list of source addresses that we refuse to accept multicast traffic from. Everything else should be forwarded.
Table of Content
Unit 1. Introduction to Multicast
Unit 2: IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol)
- Multicast IGMP Version 1
- Multicast IGMP Version 2
- Multicast IGMP Version 3
- Multicast IGMP Filter
- Multicast IGMP Proxy
Unit 3: Multicast L2
- Multicast IGMP Snooping
- IGMP Snooping without Router
- Multicast CGMP (Cisco Group Management Protocol)
Unit 4: Multicast L3
- Multicast Routing
- Multicast PIM Dense Mode
- Multicast PIM Sparse Mode
- Multicast PIM Sparse-Dense Mode
- Multicast PIM Auto RP
- Multicast PIM BSR (Bootstrap)
- RPF (Reverse Path Forwarding)
- Multicast Tunnel RPF Failure
- PIM Designated Router
- PIM Assert
- Multicast PIM Prune Override
- Multicast PIM Register Message
- Anycast RP
- Multicast MSDP SA Filtering
- Multicast Bidirectional PIM
- Multicast Stub Routing and IGMP Helper
- Source Specific Multicast
- Multicast PIM Accept RP
- Multicast PIM Accept Register
- Multicast Auto-RP Mapping agent behind Spoke
- PIM NBMA Mode
- Multicast Boundary Filtering
- Multicast PIM Snooping