Multicast IP Addresses Overview
One of the differences between unicast and multicast IP addresses is that unicast IP addresses represent a single network device while multicast IP addresses represent a group of receives. IANA has reserved the class D range to use for multicast. The first 4 bits in the first octet are 1110 in binary, meaning we have the 224.0.0.0 through 239.255.255.255 range for IP multicast addresses.
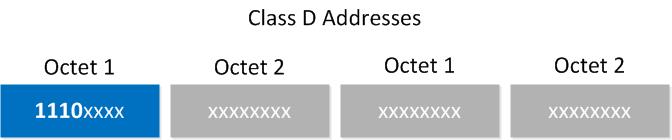
Some of the addresses are reserved, however, and we can’t use them for our own applications.
The 224.0.0.0 – 224.0.0.255 range has been reserved by IANA to use for network protocols. All multicast IP packets in this range are not forwarded by routers between subnets. Let me give you an overview of reserved link-local multicast addresses. I’m sure you recognize some of the protocols:
| Address | Usage |
| 224.0.0.1 | All Hosts |
| 224.0.0.2 | All Multicast Routers |
| 224.0.0.3 | Unassigned |
| 224.0.0.4 | DVMRP Routers |
| 224.0.0.5 | OSPF Routers |
| 224.0.0.6 | OSPF DR/BDR Router |
| 224.0.0.7 | ST Routers |
| 224.0.0.8 | ST Hosts |
| 224.0.0.9 | RIPv2 Routers |
| 224.0.0.10 | EIGRP Routers |
| 224.0.0.11 | Mobile Agents |
| 224.0.0.12 | DHCP Server / Relay |
| 224.0.0.13 | All PIM Routers |
| 224.0.0.14 | RSVP Encapsulation |
| 224.0.0.15 | All CBT Routers |
| 224.0.0.16 | Designated SBM |
| 224.0.0.17 | All SBMS |
| 224.0.0.18 | VRRP |
| 224.0.0.19 – 255 | Unassigned |
You probably recognized OSPF (224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6), RIPv2 (224.0.0.9), and EIGRP (224.0.0.10). Once you dive more into multicast, you will also encounter PIM (Protocol Independent Multicast) with 224.0.0.13.
IANA also reserved the 224.0.1.0 /24 range for certain applications. Everything in the 224.0.1.0 /24 range can be routed, however, unlike the 224.0.0.0 /24 range. Here’s an overview
Table of Content
Unit 1. Introduction to Multicast
Unit 2: IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol)
- Multicast IGMP Version 1
- Multicast IGMP Version 2
- Multicast IGMP Version 3
- Multicast IGMP Filter
- Multicast IGMP Proxy
Unit 3: Multicast L2
- Multicast IGMP Snooping
- IGMP Snooping without Router
- Multicast CGMP (Cisco Group Management Protocol)
Unit 4: Multicast L3
- Multicast Routing
- Multicast PIM Dense Mode
- Multicast PIM Sparse Mode
- Multicast PIM Sparse-Dense Mode
- Multicast PIM Auto RP
- Multicast PIM BSR (Bootstrap)
- RPF (Reverse Path Forwarding)
- Multicast Tunnel RPF Failure
- PIM Designated Router
- PIM Assert
- Multicast PIM Prune Override
- Multicast PIM Register Message
- Anycast RP
- Multicast MSDP SA Filtering
- Multicast Bidirectional PIM
- Multicast Stub Routing and IGMP Helper
- Source Specific Multicast
- Multicast PIM Accept RP
- Multicast PIM Accept Register
- Multicast Auto-RP Mapping agent behind Spoke
- PIM NBMA Mode
- Multicast Boundary Filtering
- Multicast PIM Snooping