Ques 1. What is the role of Virtual Wire interface in Palo Alto firewall?
Virtual wire is a deployment method of Palo Alto NGFW deployment, where the firewall is installed transparently on a network segment between two firewall ports and passes traffic through as layer 2. Virtual wire is internal to the firewall since it performs the change logically. We can create virtual wire sub interfaces to classify traffic according to an IP address, IP range, or subnet. The best thing about virtual wire is that it does not require any change to adjacent network devices

Ques 2. What is APP-ID?
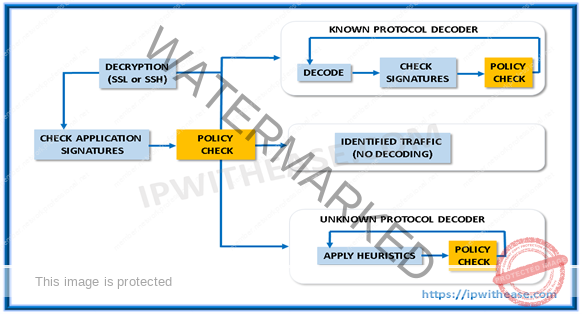
App-ID is a feature in Palo Alto NGFW which enables us to see the applications on the network and learn how they work, their behavioural characteristics and associated risks. App-ID identifies application functions via multiple methods –
- Application signatures
- Decryption
- Protocol decoding
- Heuristics.
The App-ID service can block high risk applications, as well as high risk behaviour, such as file-sharing, and traffic encrypted with the SSL protocol can be decrypted and inspected.
Ques 3. How does App-ID identify the application used in network?
Identification of the applications is the very 1st task performed by Palo Alto Networks NGFW traversing the network using App-ID. Below are the identification mechanisms–
- Application protocol detection and decryption where application protocol is determined and if SSL is in use, decrypts the traffic so that it can be analysed further.
- Application protocol decoding where it determines whether the initially detected application protocol is the actual one, or if it is being used as a tunnel to hide the actual application.
- Application signatures where Context-based signatures look for unique properties and transaction characteristics to correctly identify the application regardless of the port and protocol being used.
- Heuristics is applied for traffic that eludes identification by signature analysis. Heuristics identifies any troublesome applications, such as P2P or VoIP tools that use proprietary encryption
Ques 4. An administrator is finding it hard to manage multiple Palo Alto NGFW Firewalls. What solution should he use to simplify and centrally manage Firewalls through singly source?
Panorama is the solution. Using Panorama we can centralize policy and firewall management of a distributed network of firewalls.

Ques 5. What are key areas in which Panorama adds value?
The key benefits/ value add which can be reaped from Panorama are –
- Centralized configuration and deployment – Panorama simplifies central management and rapid deployment of the firewalls on the network. Firewalls can be assembled into groups, and templates can be created to apply on devices and use device groups to administer rules.
- Aggregated logging for analysis and reporting – 1st activity logs are collected from all the managed firewalls on the network and then centrally analysed, investigated and finally reported. A comprehensive view of network traffic, user activity, and the associated risks is showcased on Panorama.
- Distributed administration– Access can be delegated or restricted to global and local firewall configurations and policies.
Ques 6. Which Palo Alto Networks solution targets endpoint security from successful Cyber-attacks?
TRAPS
Ques 7. What are different modes in which interfaces on Palo Alto can be configured?
When configuring the Ethernet ports on your firewall, we can have option to use in one of below modes –
- Virtual wire
- Layer 2
- Layer 3 interface
Ques 8. Which command is used to Show the maximum log file size?
show system logdb-quota
Ques 9. What is function of Zone Protection profile?
Zone Protection Profiles offer protection against most common flood, reconnaissance, and other packet-based attacks. For each security zone, we can define a zone protection profile that specifies how the security gateway responds to attacks from that zone. The following types of protection are supported –
- Flood Protection – Protects against SYN, ICMP, UDP, and other IP-based flooding attacks.
- Reconnaissance detection– Allows you to detect and block commonly used port scans and IP address sweeps that attackers run to find potential attack targets.
- Packet-based attack protection –Protects against large ICMP packets and ICMP fragment attacks.

Ques 10. What is difference between Palo Alto NGFW and WAF?

Ques 11. What is U-Turn NAT?

U-Turn NAT refers to the logical path that traffic appears to travel when accessing an internal resource when they resolve their external address. U-turn NAT is mostly used in a network when internal users also need to access Web facing servers in DMZ Zone server using the server’s external public IP address.
Ques 12. Explain the difference between Virtual Routers and Virtual Systems in Palo Alto?

Ques 13. A new customer wants to setup firewall to process 10Gbps of traffic. Which firewall models could be recommended to the customer?
Below are the best possible Firewalls that can be proposed in customer environment (requiring atleast 10 Gbps throughput)
- PA-5250 (40 Gbps)
· PA-5220 (20 Gbps)
- PA-3260 (10 Gbps)
Considering that fact that Firewall will be deployed for atleast 5 to 7 years, a higher throughput is strongly recommended. For instance if 50% rise is throughput is expected (which makes total throughput requirement as 15 Gbps), PA-5220 is the most suitable candidate.
Ques 14. Which Dynamic Routing protocol cannot be configured on the Palo Alto Firewall?
EIGRP and IGRP
Ques 15. What is difference between stream-based application scanning and file-based application scanning?
Stream-based scanning is a technique that begins scanning as soon as the first packets of the file are received as opposed to waiting until the entire file is loaded into memory to begin scanning. Stream-based scanning minimizes performance and latency issues by receiving, scanning, and sending traffic to its intended destination immediately without having to first buffer and then scan the file. On the other hand, File based scanning needs to download the entire file before they can scan the traffic.

Ques 16. Which all IPS mechanisms are used for Content-ID to secure network from attacks?
IPS mechanisms used in Content-ID include –
- Protocol decoders and anomaly detection
- Stateful pattern matching
- Statistical anomaly detection
- Heuristic-based analysis
- Invalid or malformed packet detection
- IP defragmentation and TCP reassembly
- Custom vulnerability and spyware phone-home signatures
Ques 17. What widget allows administrators to quickly investigate security incidents by correlating threats with applications and user identity?
Application Command Center (ACC)
Ques 18. Which all types of logs can be viewed on Palo Alto NGFWs?
- Traffic logs.
- Threat logs.
- URL Filtering logs.
- WildFire Submissions logs.
- Data Filtering logs.
- Correlation logs.
- Config logs.
- System logs.
- HIP Match logs
- Alarms logs
- Unified logs
Ques 19. A malicious file was not blocked by WildFire evaluation and somehow was allowed to execute. Can such malicious activity still be blocked?
Yes, by Traps malware prevention modules (MPMs).
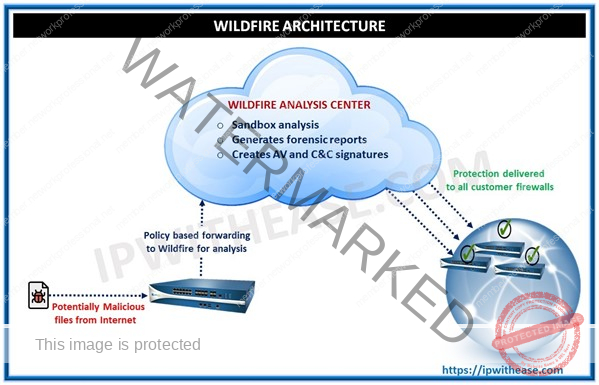
Ques 20. What is Wildfire? Explain its functioning?
WildFire provides detection and prevention of zero-day malware using a combination of malware sandboxing and signature-based detection and blocking of malware. When a Palo Alto Networks firewall detects an unknown sample, which may be a file or a link in an email, the firewall can automatically forward the sample for WildFire analysis. The sample is analysed and executed in the WildFire sandbox, where sample is determined to be benign, grayware, or malicious. WildFire then generates signatures to recognize the newly- discovered malware, and makes the latest signatures globally available every five minutes. All Palo Alto Networks firewalls can then compare incoming samples against these signatures to automatically block the malware first detected by a single firewall.
Ques 21. By default, what is the IP address of management port on Palo Alto Firewall and default username/password?
Default IP address of management port is 192.168.1.1. From a browser, go to
https://192.168.1.1 and input the Username and password as admin/admin.
Ques 22. What is the key difference between superuser and device administrator?
A Superuser administrator can create virtual systems and add a Device Administrator, vsysadmin, or vsysreader. A Device Administrator can access all virtual systems, but cannot add administrators.
Ques 23. How many virtual systems can be carved out fromPA-800?
Palo Alto Firewall does not support Virtual Systems.
Ques 24. What are the HA modes in which Palo Alto Firewall can be configured?
- Active/Passive
- Active/Active
Ques 25. What is HA Lite?
HA Lite is an active/passive deployment that provides configuration synchronization and some runtime data synchronization such as IPsec security associations. It does not support any session synchronization (HA2), and therefore does not offer Stateful failover. The PA- 200 firewall supports HA Lite only.
Ques 26. Explain Active/Active HA in Palo Alto NGFW?
Active-Active HA is supported only in Virtual-Wire and Layer 3 modes. With Active-Active deployment, both the devices are working as active in addition to processing of traffic
Active-Active HA is supported only in the virtual-wire and Layer 3 modes. This type of deployment is preferred for scenarios involving asymmetric routing. In addition to the HA1 and HA2 links used in active-passive, active-active deployments require a dedicated HA3 link. This link is used as packet forwarding link for session setup and asymmetric traffic handling.

In an active-active cluster, the packet handling is performed by 2 important functions that are handled by the devices in a cluster
- Session ownership
- Session setup
Session Ownership – Within an active–active cluster, the session owner device can be either the firewall that receives the first packet of a new session or the device in an active-primary state. This device is responsible for –
- All layer 7 processing
- Generating all traffic logs for the session
Session Setup – The session setup device is responsible for
- Layer2 through layer4 processing required for setting up a new session.
- Address translation is performed by the session setup device.
Ques 27. Explain Active/Passive HA in Palo Alto NGFW?
In scenario of Active/Passive HA, one firewall actively manages traffic while the other continuously synchronizes and always ready to transition to the active state during event of failure. In this mode, both firewalls share the same configuration settings, and one actively manages traffic. When the active firewall fails, the passive firewall transitions to the active state and takes over seamlessly and enforces the same policies to maintain network security. Active/passive HA is supported in the virtual wire, Layer 2, and Layer 3 deployments. HA1 (config sync) and HA2 (state sync) are used in Active/Passive setup, while HA3 is not required.

Ques 28. What are the different states of HA Firewall?
Different states of HA Firewall are enlisted below –
- Initial
- Active
- Passive
- Active-Primary
- Active-Secondary
- Tentative
- Non-functional
- Suspended
Ques 29. Which ports types are used in HA Pair?
- Control Link – The HA1 link is used to exchange hellos, heartbeats, and HA state information, and management plane sync for routing and User-ID information. This link is also used to synchronize configuration changes on either the active or passive device with its peer.
- Data Link—The HA2 link is used to synchronize sessions, forwarding tables, IPsec security associations and ARP tables between devices in an HA pair. Data flow always flows from the active device to the passive device.
- Backup Links – Provide redundancy for the HA1 and the HA2 links. In-band ports are used as backup links for both HA1 and HA2.
- Packet-Forwarding Link – In addition to HA1 and HA2 links, an active/active deployment also requires a dedicated HA3 link. The firewalls use this link for forwarding packets to the peer during session setup and asymmetric traffic flow. The HA3 link is a Layer 2 link that uses MAC-in-MAC encapsulation. It does not support Layer 3 addressing or encryption.
Ques 30. What are the prerequisites while configuring an HA pair?
Below are the pre-requisites for configuring an HA pair –
- The same model
- The same PAN-OS version
- The same multi virtual system capability
- The same type of interfaces
- The same set of licenses
Ques 31. The Palo Alto Networks firewall supports how many types of VPN deployments?
- Site-to-Site VPN – The simplest form of VPN that connects a central site and a remote site, or a hub and spoke VPN that connects a central site with multiple remote sites.
- Remote User-to-Site VPN – This VPN type uses the GlobalProtect agent to allow a remote user to establish a secure connection with the firewall.
- Large Scale VPN – Provides a simplified mechanism to roll out a scalable hub and spoke VPN with up to 1,024 satellite offices.
Ques 32. What is a service route? What interface is used by default to access external services?
The firewall uses the management (MGT) interface by default to access external services such as DNS servers, URL updates etc. An alternative to using the MGT interface is to configure a data port which is a regular interface, to access these services. The path from the interface to the service on a server is known as a service route. The service packets exit the firewall on the port assigned for the external service and the server sends its response to the configured source interface and source IP address.
Ques 33. How many zones can an interface be part of?
One
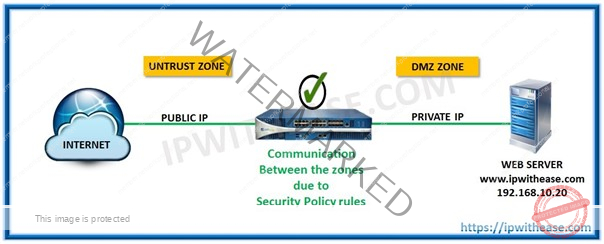
Ques 34. 2 Zones are configured on a Palo Alto Firewall. IP communication is not happening between both zones. What is required to allow this?
Security policy rule must be implemented to allow traffic flow across source zone and destination zone.

Ques 35. What interface options are available to manage Palo Alto Firewall?
- Web Interface
- Command Line Interface (CLI)
- XML API
Ques 36. Which file is mandatory for bootstrap process to function?
init‐cfg.txt
Ques 37. What is the basic approach to deploy/obtain certificates for Palo Alto Networks firewalls?
- Obtain certificates from a trusted third‐party CA
- Obtain certificates from an enterprise CA
- Generate self‐signed certificates
Ques 38. What are different types of links related for Firewall HA?
- Control Link
- Data Link
- Backup Links
- Packet-Forwarding Link
Ques 39. What parameter decides a primary and secondary HA pair?
The firewalls in an HA pair can be assigned a device priority value to indicate a preference for which firewall should assume the active or active‐primary role.
Ques 40. What is Application Command Center (ACC)?
The Application Command Center (ACC) provides insight about the activity within customer network. It is an interactive, graphical summary of traffic traversing the network. This traffic may be applications, users, URLs, threats, and content. ACC uses the firewall logs to provide visibility into traffic patterns and actionable information on threats. ACC
Ques 41. An administrator wants to configure a Palo Alto Networks NGFW to provide protection against worms and trojans. Which Security Profile type will protect against worms and trojans?
Antivirus
Ques 42. Which virtualization platforms support the deployment of Palo Alto Networks VM- Series firewalls?
- Boot Strap Virtualization Module (BSVM)
- Microsoft Hyper-V
Ques 43. A traffic log displays “incomplete” for a new application. What does that mean?
“Incomplete” signifies that new application traffic was not explicitly identified by App-ID. Further, SYN or SYN-SYNACK-ACK for this new application is seen, but no data packet are seen.
Ques 44. What are options available on Palo Alto firewall for forwarding the log messages?
- Syslog server
- SNMP manager
- Panorama
Ques 45. What happens when a URL matches multiple patterns (multiple custom URL filtering categories and allow/block-list) within a URL filtering profile?
When that happens, the category chosen is the one that has the most severe action defined as below (block being most severe and allow least severe).
- block
- override
- continue
- alert
- allow
Ques 46. What are actions available while filtering URLs?
Following are the available actions –
- Allow – Traffic is passed and no log generated
- Block – Traffic is blocked and block log generated
- Alert – Traffic is allowed and allow log generated
- Continue – User is warned that the site is questionable. Block- Continue log is generated.
- Override – Traffic is blocked. User is offered chance to enter override password. Block-Override log is generated.
Ques 47. Which are pre-defined administrator roles?
There are 6 pre-defined administrator roles:
- Superuser – All access to all options of all virtual systems.
- Superuser (read-only)
- Device Admin – Full access to the device except for creation of virtual systems and administrative accounts.
- Device admin (read-only)
- Vsys Admin – Full access to a specific virtual system.
- Vsys admin (read-only)
Ques 48. What is Captive portal and its usage?
Captive portal is a feature on Palo Alto firewall which can be used for user identification. When a user tries to access http or https sites, he will get prompted for captive portal authentication page. After providing the username and password, user will be allowed to access internet and firewall can enforce security policy.
Ques 49. How Does Panorama address new logs Logs when It Reaches Maximum Storage limit?
Panorama automatically deletes older logs to create space for new ones.
Ques 50. What is the benefit of using Splunk with Palo Alto devices?
By combining the visibility of Palo Alto products with Splunk allows to make correlations and perform analytics around different kinds of data. These correlations can be between different kinds of Palo Alto Networks data. Furthermore, Splunk is responsible for correlating and analytics across multiple sources of data and multiple vendors like correlating firewall logs with webserver logs, or advanced endpoint security logs with Windows event logs.