Private range AS numbers (64512 – 65535) should not be used on the Internet since they are not unique like public AS numbers.
Sometimes, private AS numbers are used for customer networks that are behind a single ISP. The advantage of doing this is that we will save some public AS numbers, the disadvantage is that if you ever plan to connect to another ISP, you should switch to a public AS number.
When the ISP forwards prefixes that it learns from the private AS, it will remove the private AS number before it forwards the prefix to other autonomous systems.
Cisco IOS routers support the remove-private-as command to achieve this. There are some restrictions however:
- You can only use this for eBGP neighbors.
- The private AS numbers are removed from outbound updates.
- You can only have private AS numbers in the AS path, if you have a mix of public and private AS numbers then the router won’t remove anything (there’s a solution for this though that I will demonstrate).
- If the AS path contains the AS number of the eBGP neighbor then it won’t be removed.
- If there are confederations, BGP only removes private AS numbers after the confederation part in the AS path.
Let’s take a look at the configuration!
Configuration
I will use the following 3 routers for this:
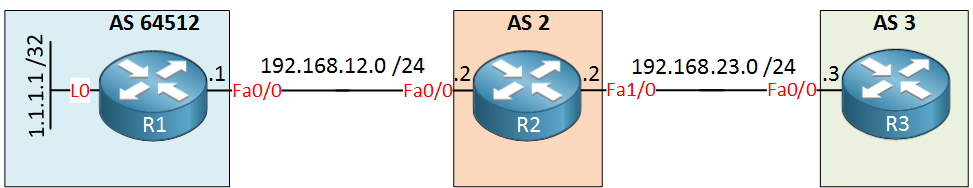
R1 is in a private AS while R2 and R3 use public AS numbers. We’ll advertise the loopback interface on R1 in eBGP so that R2 and R3 can learn it. Here’s the BGP configuration of these routers:
R1#show run | section bgp
router bgp 64512
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 1.1.1.1 mask 255.255.255.255
neighbor 192.168.12.2 remote-as 2R2#show run | section bgp
router bgp 2
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 192.168.12.1 remote-as 64512
neighbor 192.168.23.3 remote-as 3R3#show run | section bgp
router bgp 3
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 192.168.23.2 remote-as 2Remove-Private-AS
Let’s take a look at R2 and R3, they should have learned about 1.1.1.1/32:
R2#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 2, local router ID is 192.168.23.2
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, x best-external, f RT-Filter
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.1/32 192.168.12.1 0 0 64512 iR3#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 2, local router ID is 192.168.23.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, x best-external, f RT-Filter
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.1/32 192.168.23.2 0 2 64512 iIn the AS path we see AS 2 and 64512, this is as expected. Now let’s configure R2 to remove the private AS number:
R2(config)#router bgp 2
R2(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.23.3 remove-private-asWe use the remove-private-as command for this. Let’s clear BGP to speed things up:
R2#clear ip bgp *Now take a look at the BGP table of R3:
R3#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 5, local router ID is 192.168.23.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, x best-external, f RT-Filter
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.1/32 192.168.23.2 0 2 iIt’s only showing AS 2 in the AS path now, the private AS number has been removed. That’s easy enough, there are a few other things we can try however…
Remove-Private-AS All
Removing the private AS number(s) will only work if there are no public AS numbers in the AS path. To demonstrate this I will add extra AS numbers on the update from R1:
R1(config)#route-map AS_PREPEND permit 10
R1(config-route-map)#set as-path prepend 1 64513 11 64514 111I used a mix of public and private AS numbers. Let’s add these to the updates to R2:
R1(config)#router bgp 64512
R1(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.12.2 route-map AS_PREPEND outLet’s reset R2 to speed things up and check the BGP table of R2 and R3:
R2#clear ip bgp *R2#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 2, local router ID is 192.168.23.2
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, x best-external, f RT-Filter
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.1/32 192.168.12.1 0 0 64512 1 64513 11 64514 111 iR3#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 9, local router ID is 192.168.23.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, x best-external, f RT-Filter
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.1/32 192.168.23.2 0 2 64512 1 64513 11 64514 111 iAs you can see above, the AS path didn’t change. No private AS numbers have been removed because there are some public AS numbers in the AS path. Cisco IOS sees this as a misconfiguration so it won’t do anything. We can change this behavior though:
R2(config)#router bgp 2
R2(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.23.3 remove-private-as allR2#clear ip bgp *IOS 15.1T and later support the all parameter. This will remove all private AS numbers, no matter what else there is in the AS path. Let’s take another look at R3:
R3#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 11, local router ID is 192.168.23.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, x best-external, f RT-Filter
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.1/32 192.168.23.2 0 2 1 11 111 iAll private AS numbers are now gone from the BGP table, only public AS numbers remain.
Remove-Private-AS All Replace
In the previous example we removed all private AS numbers, it’s also possible to replace them with our local AS number. Here’s how:
R2(config)#router bgp 2
R2(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.23.3 remove-private-as all replace-asR2#clear ip bgp *Add the replace-as parameter behind the remove-private-as all command and that’s it. Here’s what the BGP table of R3 looks like now:
R3#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 12, local router ID is 192.168.23.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, x best-external, f RT-Filter
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.1/32 192.168.23.2 0 2 2 1 2 11 2 111 iAs you can see all private AS numbers have been replaced by AS 2. That’s all there is to it!
Unit 1: Introduction to BGP
- Introduction to BGP
- Single/Dual (multi) homed connections
- eBGP (external BGP)
- eBGP Multi-Hop
- iBGP (internal BGP)
- How to read the BGP Table
- How to advertise networks in BGP
- iBGP Next Hop Self
- BGP Auto-summary
Unit 2: BGP Neighbor Adjacency
- BGP Neighbor Adjacency States
- BGP Messages
- Troubleshooting BGP Neighbor Adjacency
- Troubleshooting BGP Route Advertisement
Unit 3: BGP Attributes
- BGP Attributes and Path Selection
- BGP Weight Attribute
- BGP Local Preference
- BGP AS Path Prepending
- BGP Origin Code
- BGP MED (metric) Attribute
Unit 4: BGP Communities
Unit 5: BGP Filtering
- BGP Regular Expressions
- BGP Transit AS
- BGP IPv6 route filtering
- BGP AS Path Filter
- BGP Extended Access-List Filtering
Unit 6: Advanced BGP Features
- BGP Peer Groups
- BGP Route Reflector
- BGP Confederations
- BGP Synchronization
- BGP Backdoor Routes
- MP-BGP (multi-protocol BGP)
- BGP Private and Public AS Numbers
- BGP Remove Private AS Numbers
- BGP 4-byte AS numbers
- BGP Soft Reconfiguration
- BGP Route Refresh Capability
- BGP Allow AS in
- BGP AS Override
- BGP Aggregate AS-SET
- BGP Multipath eBGP and iBGP