n this lesson, we’ll take a look at the BGP Confederation. As you might know, IBGP requires a full mesh of peerings which can become an administrative nightmare. If you don’t know why we need a full mesh, I recommend to start reading my IBGP lesson first.
To reduce the number of IBGP peerings, there are two techniques:
- Confederations
- Route Reflector
Let’s talk about confederations, look at the picture below:
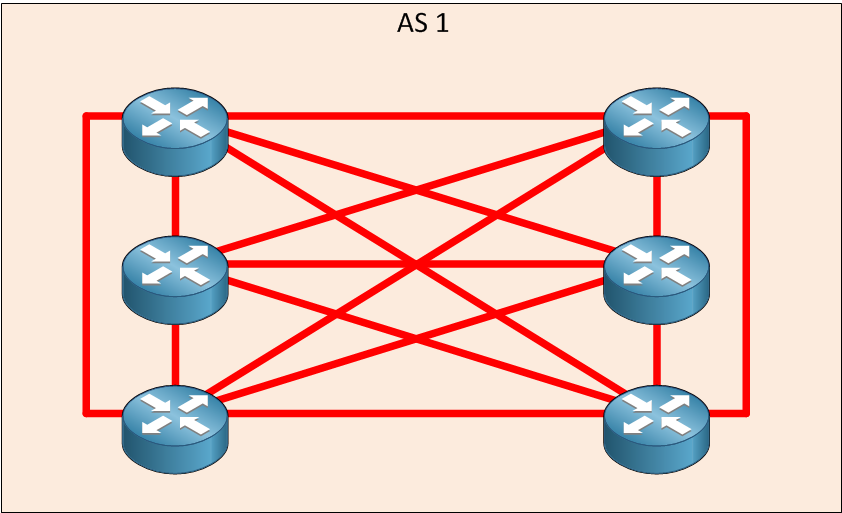
Above, we have AS 1 with six routers running IBGP. The number of IBGP peerings can be calculated with the full mesh formula:
N(N-1)/2
So, in our case, that’s:
6 * (6-1 = 5) / 2 = 15 IBGP peerings.
A BGP confederation divides our AS into sub-ASes to reduce the number of required IBGP peerings. Within a sub-AS, we still require full-mesh IBGP but between these sub-ASes we use something that looks like EBGP but behaves like IBGP (called confederation BGP) . Here’s an example of what a BGP confederation could look like:
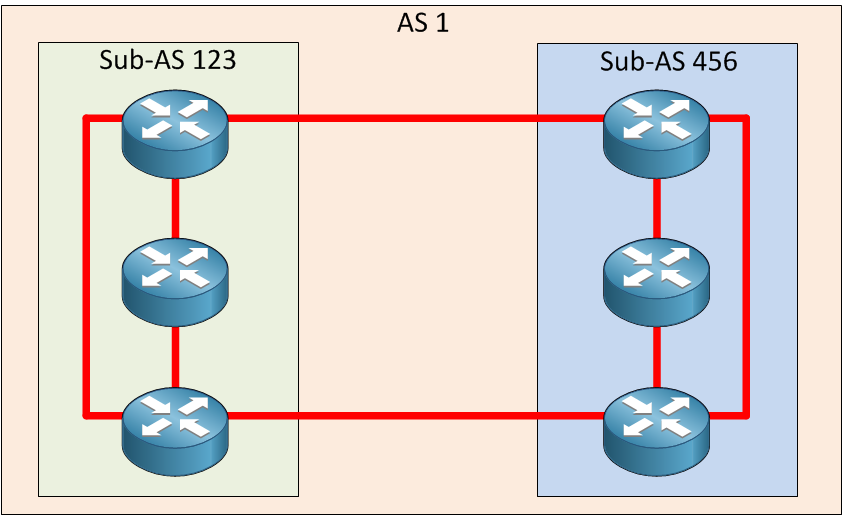
By dividing our main AS into two sub-ASes, we reduced the number of IBGP peerings from 15 to 8.
Within the sub-AS, we still have the full-mesh IBGP requirement. Between sub-ASes, it’s just like EBGP, it’s up to you how many peerings you want. The outside world will never see your sub-AS numbers. They will only see the main AS number.
Since the sub-AS numbers are not seen outside of your network, you will often see private AS numbers used for the sub-ASes (64512 – 65535), but you can pick any number you like.
Configuration
You should now have an idea of what BGP confederations are like, let’s look at the configuration so I can add some more details. I’ll use the following topology:
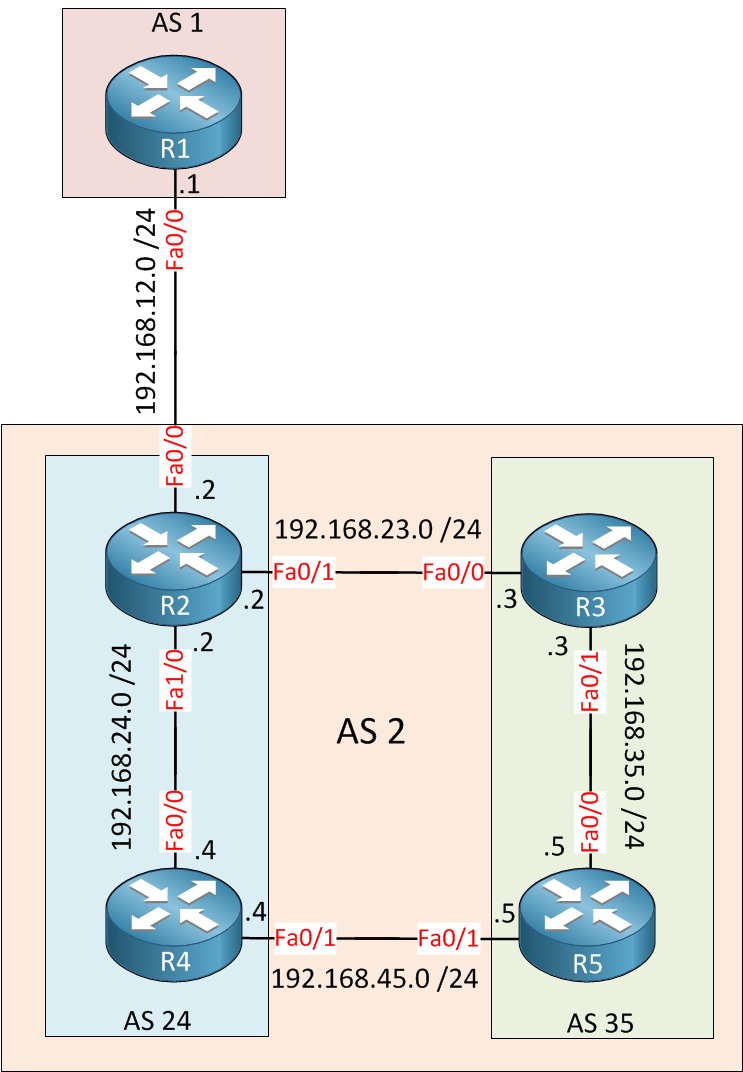
Above we have AS 2 which is divided into two sub-ASes, AS 24 and AS 35. There’s also AS 1 on top that we can use to see how the outside world sees our confederation.
Just like any other IBGP configuration, it’s best practice to use loopback interfaces for the BGP sessions. For this reason, I created a loopback interface on all routers within AS 2, and I’ll use OSPF to advertise them.
OSPF Configuration
R2(config)#router ospf 1
R2(config-router)#network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
R2(config-router)#network 192.168.24.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
R2(config-router)#network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0R3(config)#router ospf 1
R3(config-router)#network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
R3(config-router)#network 192.168.35.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
R3(config-router)#network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 area 0R4(config)#router ospf 1
R4(config-router)#network 192.168.24.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
R4(config-router)#network 192.168.45.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
R4(config-router)#network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 area 0R5(config)#router ospf 1
R5(config-router)#network 192.168.35.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
R5(config-router)#network 192.168.45.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
R5(config-router)#network 5.5.5.5 0.0.0.0 area 0Now, we can worry about the BGP confederation configuration. I’ll explain all the different steps…
BGP Confederation Configuration
Let’s start with R2:
R2(config)#router bgp 24
R2(config-router)#bgp confederation identifier 2
R2(config-router)#bgp confederation peers 35
R2(config-router)#neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 24
R2(config-router)#neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source loopback 0
R2(config-router)#neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 35
R2(config-router)#neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source loopback 0
R2(config-router)#neighbor 3.3.3.3 ebgp-multihop 2The configuration of R2 requires some explanation. First of all, when you start the BGP process, you have to use the AS number of the sub-AS. Secondly, you have to use the bgp confederation identifier command to tell BGP what the main AS number is.
We also have to configure all other sub-AS numbers with the bgp confederation peers command, in this case, that’s only AS 35. R4 is in the same sub-as, so you can configure this neighbor just like any other IBGP neighbor. R3 is a bit different, though…since it’s in another sub-AS, we have to use the same rules as EBGP, which means configuring multihop if you are using loopbacks.
Let’s take a look at R3:
R3(config)#router bgp 35
R3(config-router)#bgp confederation identifier 2
R3(config-router)#bgp confederation peers 24
R3(config-router)#neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 24
R3(config-router)#neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source loopback 0
R3(config-router)#neighbor 2.2.2.2 ebgp-multihop 2
R3(config-router)#neighbor 5.5.5.5 remote-as 35
R3(config-router)#neighbor 5.5.5.5 update-source loopback 0The configuration of R3 is similar to R2. We configure it to use AS 35 while the main AS is 2. Our only sub-AS peer is 24, and we have two neighbors…one IBGP neighbor and one “EBGP” (confederation BGP) neighbor.
R4 and R5 look pretty much the same:
R4(config)#router bgp 24
R4(config-router)#bgp confederation identifier 2
R4(config-router)#bgp confederation peers 35
R4(config-router)#neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 24
R4(config-router)#neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source loopback 0
R4(config-router)#neighbor 5.5.5.5 remote-as 35
R4(config-router)#neighbor 5.5.5.5 update-source loopback 0
R4(config-router)#neighbor 5.5.5.5 ebgp-multihop 2R5(config)#router bgp 35
R5(config-router)#bgp confederation identifier 2
R5(config-router)#bgp confederation peers 24
R5(config-router)#neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 24
R5(config-router)#neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source loopback 0
R5(config-router)#neighbor 4.4.4.4 ebgp-multihop 2
R5(config-router)#neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 35
R5(config-router)#neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source loopback 0That takes care of configuring the neighbors. The more interesting part is, of course, using some show commands to see the differences between normal IBGP and EBGP. Let’s get going…
Verification
To have something we can look at, I will create a loopback interface on R5 and advertise a network in BGP:
R5(config)#interface loopback 5
R5(config-if)#ip address 55.55.55.55 255.255.255.255Let’s advertise it in BGP:
R5(config)#router bgp 35
R5(config-router)#network 55.55.55.55 mask 255.255.255.255Let’s look at R3 first. This router is in the same sub-AS as R5:
R3#show ip bgp 55.55.55.55
BGP routing table entry for 55.55.55.55/32, version 2
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Flag: 0x820
Advertised to update-groups:
2
Local
5.5.5.5 (metric 2) from 5.5.5.5 (5.5.5.5)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, confed-internal, bestThis entry looks pretty much the same as normal IBGP, but there’s one important difference…
The route is tagged with confed-internal which means that it came from an IBGP router within the same sub-AS. Let’s check R2 now:
R2#show ip bgp 55.55.55.55
BGP routing table entry for 55.55.55.55/32, version 2
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Flag: 0x820
Advertised to update-groups:
2
(35)
5.5.5.5 (metric 3) from 3.3.3.3 (3.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, confed-external, bestBGP confederations use a new BGP attribute called AS_CONFED_SET. This “confederation set” prepends the list with the sub-ASes. Above, you can see (35), which means that this route came from another sub-AS (35). Prepending occurred when R3 sent the update to R2.
When this route is sent to another AS, all the sub-AS numbers will be removed. Let’s see how that works…I didn’t configure EBGP between R1 and R2 yet, so let’s do that now:
R1(config)#router bgp 1
R1(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.12.2 remote-as 2R2(config)#router bgp 24
R2(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.12.1 remote-as 1Let’s see what R1 in AS 1 thinks of the 55.55.55.55/32 route:
R1#show ip bgp 55.55.55.55
BGP routing table entry for 55.55.55.55/32, version 2
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Flag: 0x820
Not advertised to any peer
2
192.168.12.2 from 192.168.12.2 (2.2.2.2)
Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, external, bestR1 only sees AS 2, so all the sub-AS magic remains within the BGP confederation. Pretty neat, right? Let’s try one more thing…I’ll advertise something on R1 so our confederation can learn about it. I’ll create a loopback and advertise it in BGP:
R1(config)#interface loopback 1
R1(config-if)#ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255R1(config)#router bgp 1
R1(config-router)#network 11.11.11.11 mask 255.255.255.255There’s one more thing we have to do…since the next hop doesn’t change with iBGP, our routers will not know how to reach 192.168.12.1 (R1). I’ll fix this by advertising the 192.168.12.0 /24 network in BGP:
R2(config)#router bgp 24
R2(config-router)#network 192.168.12.0 mask 255.255.255.0An alternative to advertising this network into iBGP is to use BGP next-hop-self.
Now let’s take a look at R2:
R2#show ip bgp 11.11.11.11
BGP routing table entry for 11.11.11.11/32, version 3
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Flag: 0x820
Advertised to update-groups:
1 2
1
192.168.12.1 from 192.168.12.1 (192.168.12.1)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external, bestThis is just plain EBGP information, nothing special. Let’s look at R4, which is in the same sub-AS:
R4#show ip bgp 11.11.11.11
BGP routing table entry for 11.11.11.11/32, version 9
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Flag: 0x820
Advertised to update-groups:
1
1
192.168.12.1 (metric 2) from 2.2.2.2 (2.2.2.2)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, confed-internal, bestR4 sees the route and recognizes it as “confed-internal”. Let’s check R3, which is a bit more interesting:
R3#show ip bgp 11.11.11.11
BGP routing table entry for 11.11.11.11/32, version 6
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to update-groups:
1
(24) 1
192.168.12.1 (metric 2) from 2.2.2.2 (2.2.2.2)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, confed-external, bestR3 is in a different sub-AS than R2. You can see that it says confed-external. Something important to note is that the next hop IP address didn’t change. When you use regular EBGP, a router changes the next hop IP address of a route to its own IP address when it sends the route to another EBGP router.
The sub-AS number from R2 has been prepended, and the AS path is now (24) 1.
If you have played with BGP and regular expressions before, see if you can create some that match the sub-AS values…nice exercise!
Let’s check the last router, R5:
R5#show ip bgp 11.11.11.11
BGP routing table entry for 11.11.11.11/32, version 6
Paths: (2 available, best #2, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to update-groups:
2
(24) 1
192.168.12.1 (metric 3) from 4.4.4.4 (4.4.4.4)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, confed-external
(24) 1
192.168.12.1 (metric 3) from 3.3.3.3 (3.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, confed-internal, bestR5 has two options: it learns about this route from R3 (confed-internal) or R4 (confed-external). The BGP best path selection algorithm has no distinction between confederation external or internal. In this case, the path was chosen based on the lowest router ID.
That’s all I have about BGP confederations for now. I hope this has been helpful to you. If you still have any questions, feel free to leave a comment.
Unit 1: Introduction to BGP
- Introduction to BGP
- Single/Dual (multi) homed connections
- eBGP (external BGP)
- eBGP Multi-Hop
- iBGP (internal BGP)
- How to read the BGP Table
- How to advertise networks in BGP
- iBGP Next Hop Self
- BGP Auto-summary
Unit 2: BGP Neighbor Adjacency
- BGP Neighbor Adjacency States
- BGP Messages
- Troubleshooting BGP Neighbor Adjacency
- Troubleshooting BGP Route Advertisement
Unit 3: BGP Attributes
- BGP Attributes and Path Selection
- BGP Weight Attribute
- BGP Local Preference
- BGP AS Path Prepending
- BGP Origin Code
- BGP MED (metric) Attribute
Unit 4: BGP Communities
Unit 5: BGP Filtering
- BGP Regular Expressions
- BGP Transit AS
- BGP IPv6 route filtering
- BGP AS Path Filter
- BGP Extended Access-List Filtering
Unit 6: Advanced BGP Features
- BGP Peer Groups
- BGP Route Reflector
- BGP Confederations
- BGP Synchronization
- BGP Backdoor Routes
- MP-BGP (multi-protocol BGP)
- BGP Private and Public AS Numbers
- BGP Remove Private AS Numbers
- BGP 4-byte AS numbers
- BGP Soft Reconfiguration
- BGP Route Refresh Capability
- BGP Allow AS in
- BGP AS Override
- BGP Aggregate AS-SET
- BGP Multipath eBGP and iBGP